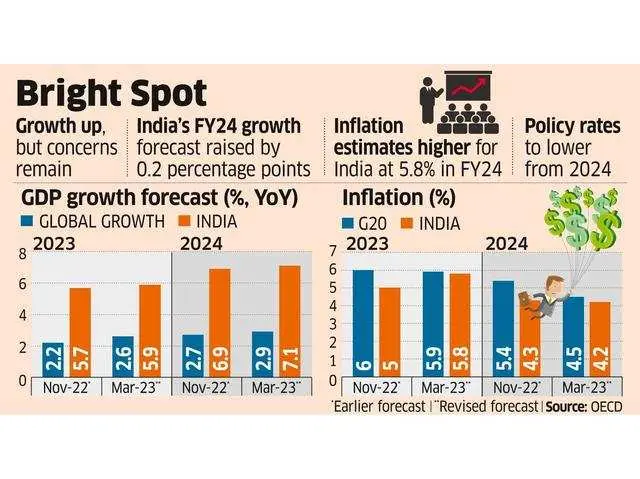
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) recently released its latest report on India, providing an in-depth analysis of the country’s economic performance, policy challenges, and future outlook. This report, offering a comprehensive overview of India’s economic landscape as assessed by the OECD.The OECD report highlights that India has demonstrated robust economic growth, particularly as the world recovers from the COVID-19 pandemic. The country’s GDP growth rate has been one of the highest among major economies, driven by strong domestic demand, government reforms, and a resilient services sector. The report underscores that despite global economic uncertainties, India’s economy is projected to continue growing at a healthy pace.

However, the report also notes that India’s growth is not without its challenges. Inflation remains a concern, fueled by rising commodity prices and supply chain disruptions. The OECD emphasizes the need for India to manage inflationary pressures carefully to sustain its growth momentum.
Structural Reforms and Policy Initiatives
The OECD commends India for its ongoing structural reforms aimed at boosting economic efficiency and competitiveness. Key reforms highlighted include the implementation of the Goods and Services Tax (GST), efforts to improve ease of doing business, and initiatives to attract foreign direct investment (FDI). These reforms are seen as critical to creating a more integrated and efficient market in India.
Furthermore, the report points to the success of digital initiatives like Aadhaar, the Unified Payments Interface (UPI), and the Digital India campaign in transforming the economy. These digital transformations have not only enhanced financial inclusion but also streamlined government services and reduced corruption.
Labor Market and Employment
A significant portion of the OECD report is dedicated to the labor market challenges in India. Despite the country’s strong economic growth, unemployment and underemployment remain persistent issues. The report highlights the need for policies that promote job creation, particularly in the manufacturing and services sectors.
The OECD suggests that improving labor market flexibility, enhancing vocational training, and aligning educational outcomes with industry needs are crucial steps to address these challenges. The report also emphasizes the importance of boosting female labor force participation, which remains low compared to other emerging economies.
Social and Environmental Challenges
The OECD report acknowledges the progress India has made in addressing social challenges, such as poverty reduction and improving access to healthcare and education. However, it also points out that significant disparities remain, particularly in rural areas and among marginalized communities.
On the environmental front, the report praises India’s commitment to renewable energy and its efforts to combat climate change. India’s ambitious targets for solar and wind energy capacity are highlighted as positive steps toward a more sustainable future. However, the OECD also warns that India needs to accelerate its efforts to reduce air pollution and manage water resources more effectively to ensure long-term environmental sustainability.
Fiscal Policy and Public Debt
The OECD report provides a detailed analysis of India’s fiscal policy and public debt situation. It acknowledges the government’s efforts to maintain fiscal discipline while supporting economic recovery through targeted spending. The report suggests that India should continue to focus on fiscal consolidation once the economic recovery is firmly established.
Public debt levels, which have risen due to the pandemic, are identified as a concern. The OECD recommends that India should aim to stabilize and gradually reduce its debt-to-GDP ratio through prudent fiscal management and efficient public spending. Enhancing tax compliance and broadening the tax base are also suggested as measures to improve fiscal health.
Trade and Global Integration
India’s role in global trade and its integration into the world economy are key themes in the OECD report. The report notes that while India has made strides in improving its trade infrastructure and policies, there is room for further liberalization. Reducing trade barriers and enhancing trade facilitation measures are recommended to boost exports and attract more investment.
The OECD also highlights the importance of regional trade agreements and suggests that India should actively participate in global trade discussions to secure favorable terms and access to new markets. Strengthening trade ties with neighboring countries and major trading partners is seen as essential for sustaining long-term economic growth.
Innovation and Digital Economy
Innovation and the digital economy are recognized as critical drivers of India’s future growth. The OECD report applauds India’s advancements in technology and digital infrastructure, which have the potential to transform various sectors of the economy. Investments in research and development (R&D), fostering a culture of innovation, and supporting startups are recommended to capitalize on this potential.
The report also emphasizes the need for robust data protection laws and cyber security measures to build trust in digital services. Ensuring that digital growth is inclusive and benefits all segments of society is highlighted as a priority.
Education and Skills Development
Education and skills development are crucial for sustaining India’s economic growth and addressing its labor market challenges. The OECD report stresses the importance of reforming the education system to improve quality and access. Enhancing vocational training programs and aligning them with market needs are seen as vital for equipping the workforce with relevant skills.
The report also underscores the need for increased investment in education, particularly in rural areas and for disadvantaged groups. Promoting lifelong learning and continuous skill development is recommended to ensure that the workforce remains adaptable and competitive in a rapidly changing global economy.
Conclusion
The OECD report on India paints a comprehensive picture of a country on the move, with significant achievements and ongoing challenges. India’s robust economic growth, driven by structural reforms and digital advancements, positions it as a key player in the global economy. However, managing inflation, addressing labor market issues, ensuring fiscal sustainability, and tackling social and environmental challenges are crucial for sustaining this growth.
The report’s recommendations provide a roadmap for India to enhance its economic resilience, inclusivity, and sustainability. By continuing to implement sound policies and reforms, India can build on its strengths and address its weaknesses, ensuring a prosperous future for its people. The OECD’s analysis and insights serve as valuable guidance for policymakers, businesses, and stakeholders as they navigate the complex landscape of India’s economic development.




Leave a Reply