Rising Temperatures and The Longest Ever Heatwave in India, is having severe repercussions on the environment, economy, and public health. It is symptomatic of broader climatic shifts driven by global warming and pose significant challenges for the region.
India has historically been prone to high temperatures and heatwaves. However, the current heatwave is exceptional in both its intensity and duration. Temperatures have soared above 45°C (113°F) in many areas, with some regions experiencing prolonged spells of temperatures exceeding 50°C (122°F). This heatwave has broken numerous historical records and is considered the longest and most severe in the region’s history.
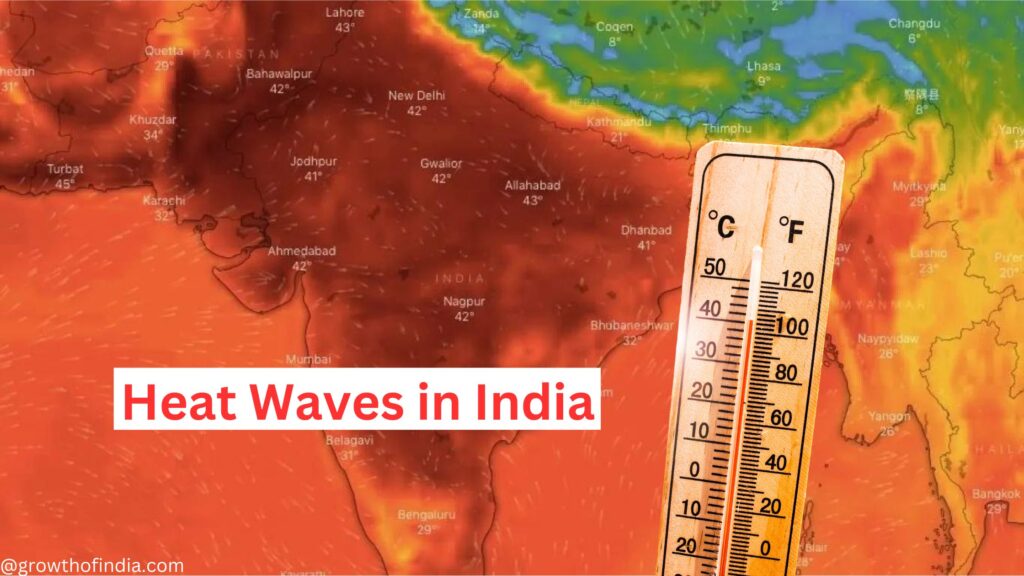
Several factors contribute to this extreme weather phenomenon:
- Climate Change: The most significant factor is global warming. The increase in greenhouse gas emissions has led to a rise in average global temperatures. In the Indian subcontinent, this has resulted in more frequent and intense heatwaves.
- Urbanization: Rapid urbanization and the proliferation of concrete structures have led to the urban heat island effect, where urban areas become significantly warmer than their rural surroundings. This exacerbates the impact of heatwaves in cities.
- Deforestation: The loss of forest cover reduces the natural cooling effects of vegetation and increases the heat absorption of the land.
- Atmospheric Circulation Patterns: Changes in atmospheric circulation patterns, influenced by both natural variability and human activities, can lead to stagnant air and prolonged heatwaves.
The environmental impacts of the heatwave are profound. Rivers and lakes are drying up, leading to water shortages for both human consumption and agriculture. The heat stresses on flora and fauna are immense, with many species struggling to survive in the extreme conditions. Forest fires, exacerbated by the dry and hot conditions, are becoming more frequent, leading to the loss of biodiversity and further contributing to air pollution.
The economic consequences of the heatwave are equally severe. Agriculture, a primary livelihood for millions in the region, is particularly hard hit. Crops are withering under the intense heat, leading to reduced yields and threatening food security. Livestock, too, is suffering, impacting dairy and meat production.
The energy sector is under immense strain as the demand for electricity surges due to increased use of air conditioning and cooling systems. This demand often leads to power outages and increased operational costs for industries. Additionally, infrastructure such as roads and railways is at risk of damage due to the extreme heat, leading to higher maintenance costs.
The heatwave is a public health emergency. Heat-related illnesses, such as heatstroke and dehydration, are on the rise. Vulnerable populations, including the elderly, children, and those with pre-existing health conditions, are at heightened risk. Hospitals are overwhelmed with cases, and there are reports of increased mortality due to the heat.
Moreover, the prolonged heatwave exacerbates existing health issues such as cardiovascular and respiratory problems. The extreme temperatures also increase the risk of vector-borne diseases, as mosquito populations thrive in the warmer climate.
Addressing the challenges posed by the heatwave requires a multi-faceted approach:
- Improved Infrastructure: Developing heat-resistant infrastructure, including green buildings and shaded public spaces, can help mitigate the impact of heatwaves.
- Water Management: Implementing efficient water management practices, such as rainwater harvesting and improved irrigation techniques, is crucial to addressing water scarcity.
- Afforestation and Urban Greenery: Planting trees and creating urban green spaces can reduce the urban heat island effect and provide cooling.
- Public Awareness and Health Services: Raising awareness about heat-related illnesses and improving public health services can help mitigate the health impacts of heatwaves.
- Renewable Energy: Investing in renewable energy sources can reduce greenhouse gas emissions and help combat climate change.
Rising Temperatures and The Longest Ever Heatwave in India is a stark reminder of the realities of climate change and its far-reaching impacts. The region must adopt comprehensive adaptation and mitigation strategies to cope with the rising temperatures. By addressing the root causes and implementing effective solutions, the Indian subcontinent can build resilience against future heatwaves and safeguard the well-being of its population and environment.





Leave a Reply